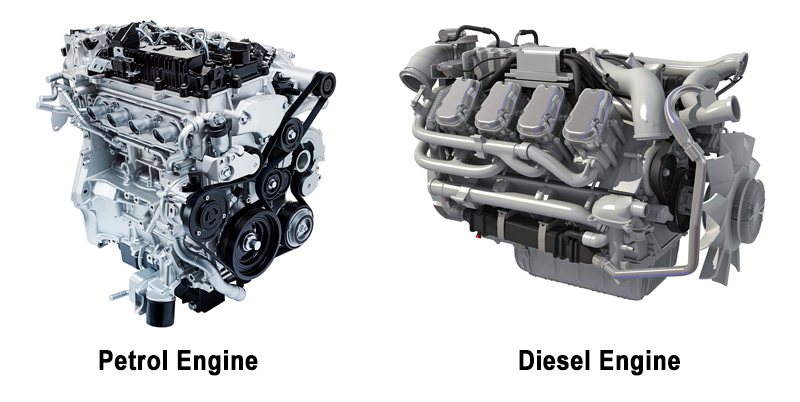
The primary difference between Petrol and Diesel engines is that the Petrol engine works on the Otto cycle whereas the Diesel engine works on the Diesel cycle. Other differences can be attributed to the structure, types, and uses of these engines. The main parameter they are classified on is the type of fuel they use. Generally, Engines run on the principle of heat transfer.
Apart from the type of fuel used, the engines are also divided on the basis of a lot of things, such as the presence of a spark plug in Petrol engines and a fuel injector in Diesel engines. We also know that lighter vehicles such as motorcycles, scooters, and cars typically use petrol in their engines whereas Diesel is used in much heavier machinery such as tractors, trucks, and buses. Thus, the types of fuel used also plays a major role in defining the major difference between Petrol and Diesel engines.
Diesel Engine
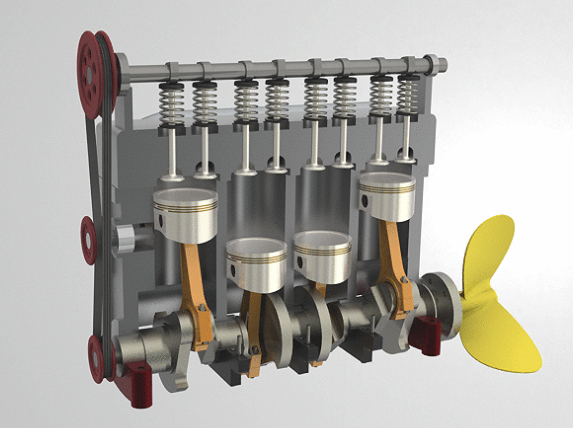 The Diesel engine is also an internal combustion engine which is also known as the compression-ignition engine. It is named after Rudolf Diesel.
The Diesel engine is also an internal combustion engine which is also known as the compression-ignition engine. It is named after Rudolf Diesel.- In these engines, the fuel is injected into a combustion chamber and is then ignited by the high temperature of the air in the chamber.
- The high temperature of the air in the cylinder is due to the adiabatic compression. These engines only compress the air and not the fuel.
- When injected into the combustion chamber, the Diesel fuel undergoes spontaneous ignition.
- These engines work on the Diesel cycle, which consists of a constant pressure process, a constant volume process, and two isentropic processes.
Petrol Engine
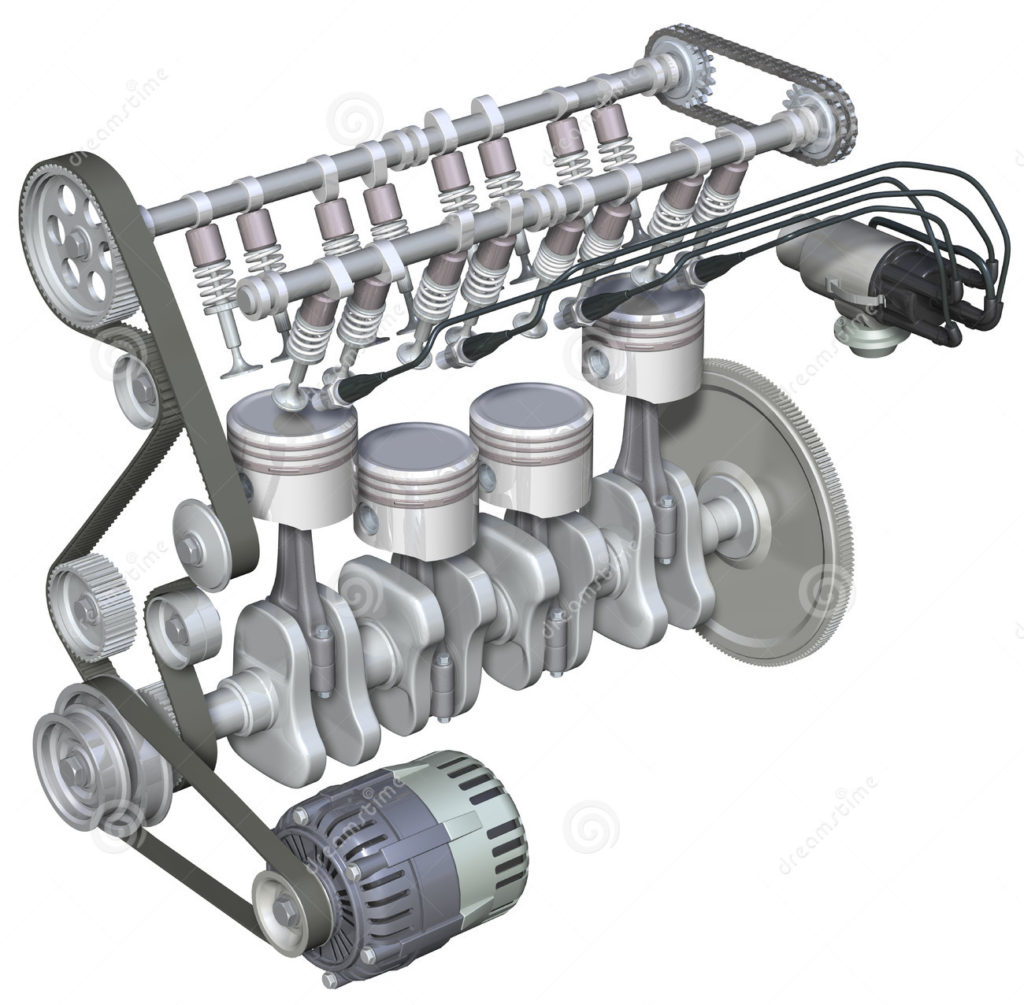 Petrol engines are internal combustion engines that have spark-ignition. They run on relatively volatile fuels such as petrol.
Petrol engines are internal combustion engines that have spark-ignition. They run on relatively volatile fuels such as petrol.- In these engines, air and fuel are generally mixed post-compression.
- Petrol engines work on the Otto cycle, which consists of two isochoric processes and two isentropic processes.
- In petrol engines, air and petrol are usually mixed in a carburetor before being introduced to the cylinder.
- Once the air and petrol are compressed, the fuel is ignited via an electric spark.
Difference |
|
| Diesel Engine | Petrol Engine |
| These engines work on the Diesel cycle | Works on the Otto cycle |
| The fuel is mixed with air inside the cylinder | Air and fuel are mixed in a carburettor |
| Ignition is achieved with the help of hot, compressed air. | Fuel is ignited with an electric spark |
| High compression ratio | Relatively low compression ratio |
| High power production | Relatively low amounts of power are produced in a Petrol engine |
| These engines work with fuels that have low volatilities | Highly volatile fuels are used in these internal combustion engines |
| Generally used in heavy vehicles such as trucks and buses | Used in light vehicles such as motorcycles and cars. |
| Relatively low fuel consumption | High fuel consumption. |
| High initial and maintenance costs | Comparatively low initial cost and maintenance cost |












[…] your temperature gauge; if the heat rises and the car stalls, this may mean the fuel pump motor is having problems. If it continues to stall out, this is a clear sign that the f-pump may be starting to […]