On the basis of the method of fuel injection the engines are classified as:
- Carburetor engine
- Air injection engine
- Airless or solid injection engine
Carburetor engine
The carburetor is responsible for mixing gasoline and air together in just the right amounts and getting that mixture into the cylinders. Though they are not found in new cars, carburetors have delivered fuel into the engines of every vehicle from legendary race cars to top-end luxury cars. They were used in NASCAR up until 2012 and many classic car enthusiasts use carbureted vehicles every single day. With that many die-hard enthusiasts, carburetors must offer something special to those who love cars. A carburetor relies on the vacuum created by the engine to draw air and fuel into the cylinders. This system was used for so long because of the simplicity behind it. The throttle can open and close, allowing either more or less air to enter the engine. This air moves through a narrow opening called a venture. This creates the vacuum required to keep the engine running.
A carburetor relies on the vacuum created by the engine to draw air and fuel into the cylinders. This system was used for so long because of the simplicity behind it. The throttle can open and close, allowing either more or less air to enter the engine. This air moves through a narrow opening called a venture. This creates the vacuum required to keep the engine running.
Air injection engine
An air injection system forces fresh air into the exhaust ports of the engine to reduce HC and CO emissions. The exhaust gases leaving an engine can contain unburned and partially burned fuel. Oxygen from the air injection system causes this fuel to continue to burn. The major parts of the system are the air pump, the diverter valve, the air distribution manifold, and the air check valve.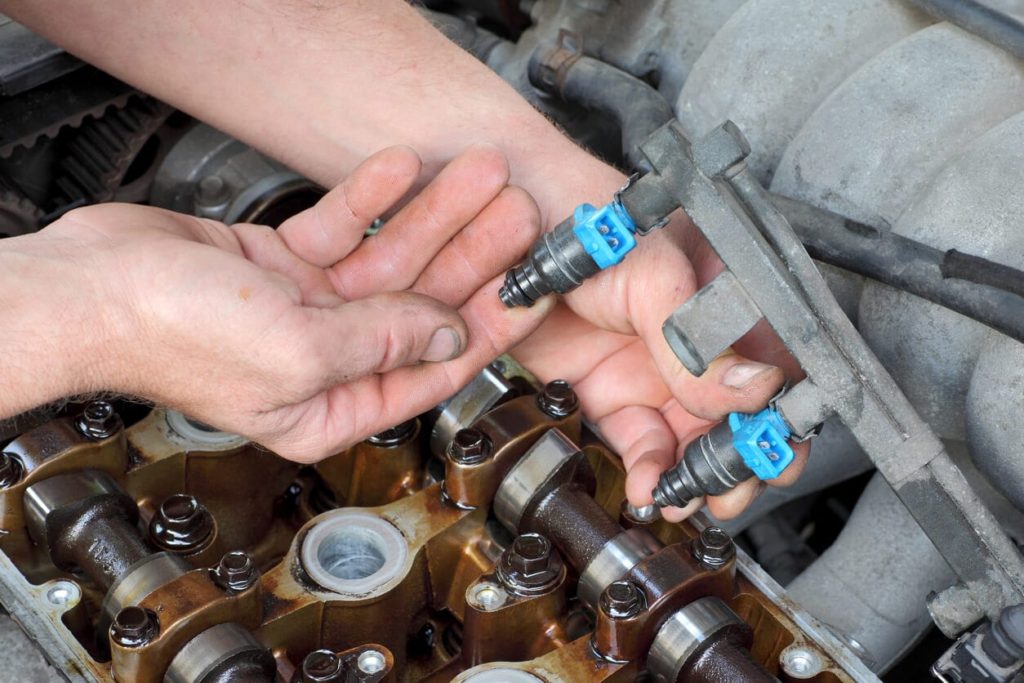 Fuel needs pressurized air to burn, but as it’s being expelled from the engine it’s surrounded mainly by gases. The air injection smog pump pushes air into the exhaust system right after the exhaust manifold, to help intercept and burn those unburned fuels. The system is critical to help cars achieve government emissions standards. So, the law says you need a secondary air injection system.
Fuel needs pressurized air to burn, but as it’s being expelled from the engine it’s surrounded mainly by gases. The air injection smog pump pushes air into the exhaust system right after the exhaust manifold, to help intercept and burn those unburned fuels. The system is critical to help cars achieve government emissions standards. So, the law says you need a secondary air injection system.
Airless or solid injection engine
A method of supplying fuel to the combustion chamber of an internal-combustion engine with internal mixing; the fuel is atomized as it enters the chamber at high speed. Direct injection is achieved by means of manifold fuel feed equipment operating at a maximum injection pressure of up to 100 meganewtons per sq m (MN/m2; 1 MN/m2 = 10 kilograms-force per sq cm) or by a pump-and-injector unit at a pressure of up to 200 MN/m2. Direct injection is used in diesel engines and in certain types of engines with spark ignition. 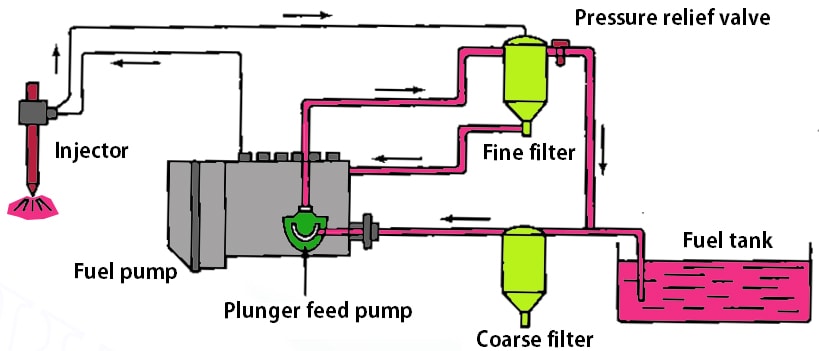 A fuel injection system for a diesel engine in which a pump forces fuel through a fuel line and an atomizing nozzle into the combustion chamber.
A fuel injection system for a diesel engine in which a pump forces fuel through a fuel line and an atomizing nozzle into the combustion chamber.
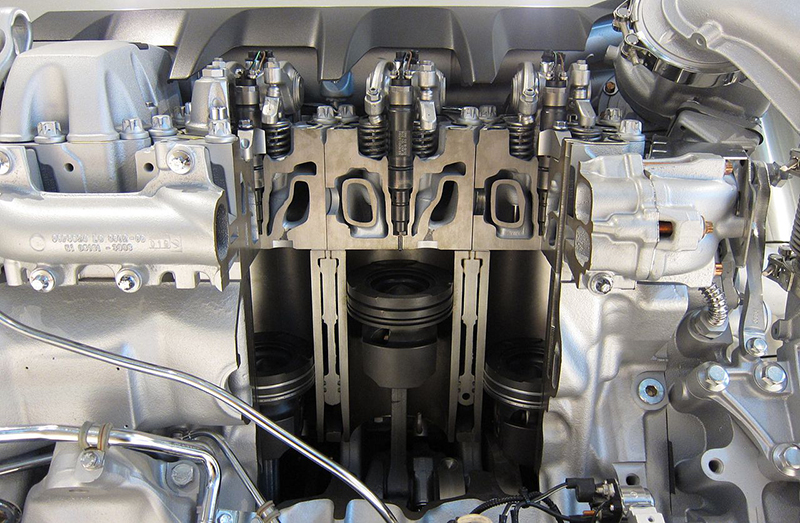












[…] This is the perfect time to run a visual diagnostic on your vehicle and make a shortlist of maintenance tasks you need to complete, so you won’t be cleaning your injectors for no […]
[…] injectors control the amount of fuel delivered to the combustion chamber. When the parts go bad, you might notice your car shakes when the engine […]
[…] and Fuel injector both are the devices used to make an air-fuel mixture and provide it to the engine. The […]
[…] is unfavorably higher than the outside. Always switch the AC on at low speed in order to draw the outside air and if you are thinking that switching the AC on the maximum level will make it quick, then you […]
[…] it withstand high pressures? You need grease that will withstand the high pressures in a wheel. Sometimes the manufacturer will […]
[…] these engines, the fuel is injected into a combustion chamber and is then ignited by the high temperature of the air in the […]
[…] new car you bought, but the manager stops you. He suggests undercoating your vehicle before you leave, and explains that it can be done right at the Kiamotors-Portqasim dealership, for a fee. You […]
[…] government generates a high amount of profit from local cars because the local car’s price is low rather than the imported […]